MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION: MUTATION
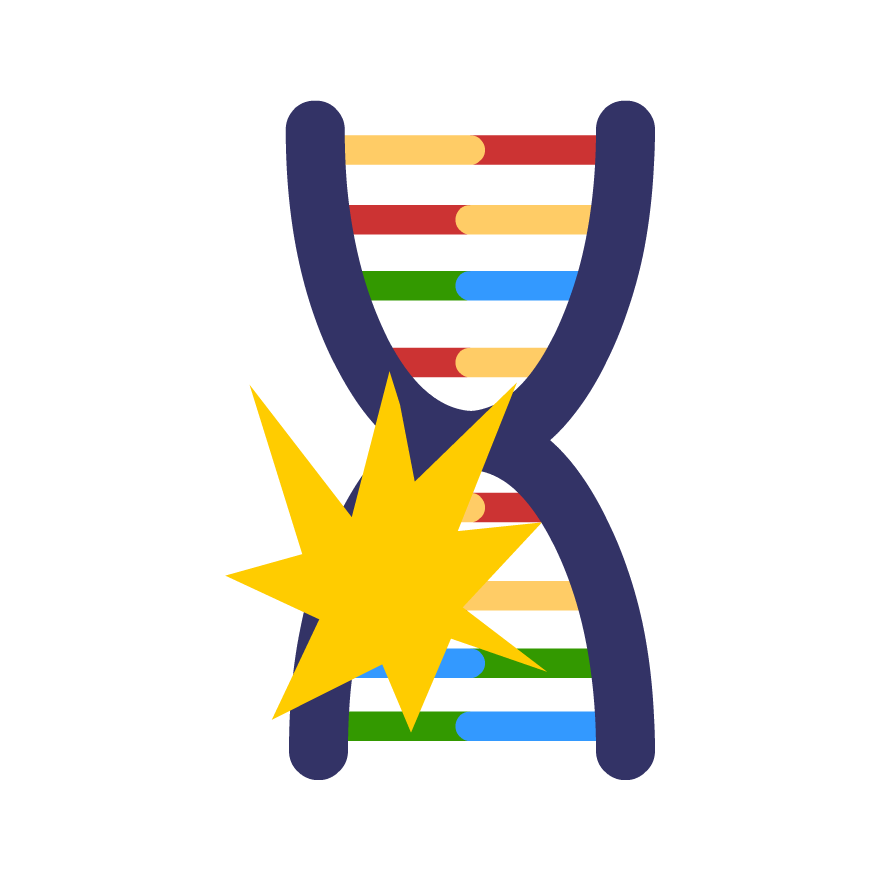

Mutation is the mechanism of evolution that deals in a random change in the DNA of an organism. These changes can range from something small and unimportant, like a cat having different colored eyes, to something big like a cat having resistance to a certain disease. Mutations do not always serve much of a purpose and can just result in small quirks. Only mutations that pass onto offspring matter to large-scale evolution, any other mutation would not make a difference in a species evolving.
MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION: GENETIC DRIFT
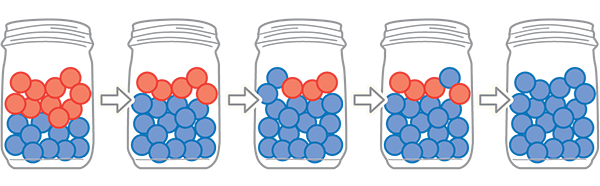
Genetic drift is the mechanism of evolution that is led by chance. Naturally, some animals do not reproduce the same amount as other animals of the same generation. Not necessarily because they lack an advantage that the other organisms in the same generation have, but because it is bound to happen. Every population of organisms eventually have genetic drift. While not all too important to evolution in the greater scale, it matters because it affects the genes of populations but only due to chance.
MECHANISMS OF EVOLUTION: GENE FLOW

Genetic flow (or also known more commonly as migration) is the mechanism of evolution that involves the movement of organisms from one population to another, often mixing genes with the new population. Genes that hadn't existed in an population beforehand would be introduced from all of the new organisms carrying unique genetic material. This increases genetic variation and thus is important to future evolution.